LiFePO4 vs. Sodium-Ion Batteries for Energy Storage: Pros, Cons, and Future Trends
LiFePO4 vs. Sodium-Ion Batteries for Energy Storage: Pros, Cons, and Future Trends
As a Chinese manufacturer specializing in home energy storage batteries with OEM capabilities, we're excited to share insights on LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) and Sodium-Ion batteries—two promising technologies for B2B applications in renewable energy. Based on 2025 market data, here's a concise comparison to inform your sourcing decisions.
LiFePO4 Batteries: Proven Reliability
Advantages:
- Exceptional lifespan: 2,000-5,000 cycles, far outlasting traditional lithium-ion (typically 1,000-2,000).
- Superior safety: High thermal stability reduces overheating risks, with no cobalt for eco-friendliness.
- Efficiency: 90-98% energy efficiency, ideal for solar integration.
- Lightweight: 50-70% lighter than lead-acid equivalents.
Disadvantages:
- Lower energy density: 120-180 Wh/kg vs. 200-250 Wh/kg for NMC batteries, limiting compact applications.
- Higher upfront cost: $200-400/kWh, though ROI improves over time.
- Suboptimal low-temperature performance: Efficiency drops below 0°C.
Sodium-Ion Batteries: Emerging Cost Leader
Advantages:
- Cost-effective: Sodium abundance cuts material costs by 30-50% vs. lithium ($50-150/kWh).
- Environmental benefits: No rare metals, reducing supply chain risks.
- Cold-weather resilience: Operates efficiently down to -20°C, outperforming lithium by 20-30% in sub-zero conditions.
- Safety: Lower fire risk due to stable chemistry.
Disadvantages:
- Lower energy density: 100-160 Wh/kg, 20-40% below LiFePO4.
- Shorter cycle life: 1,000-3,000 cycles, degrading faster than LiFePO4.
- Immature scalability: Higher production challenges, with efficiency at 80-90%.
Future Trends (2025-2030)
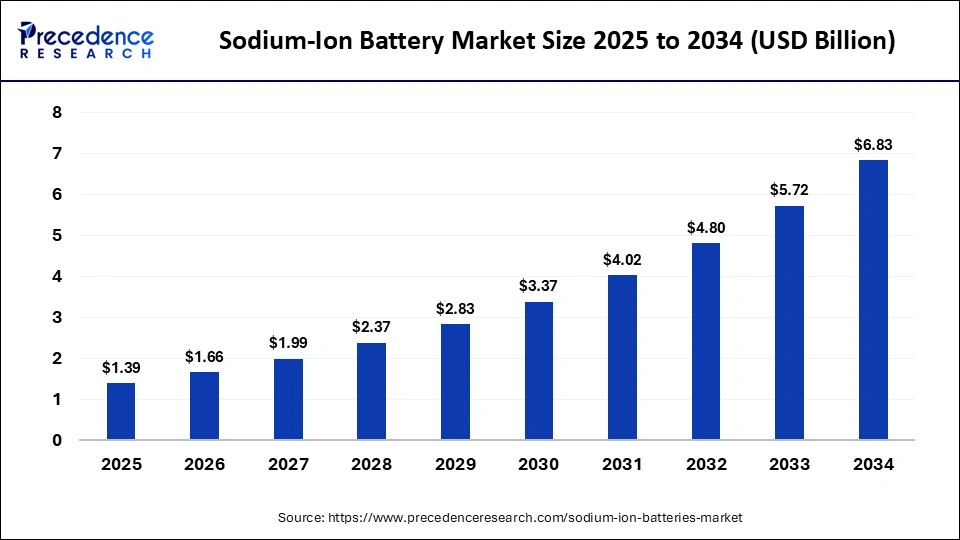
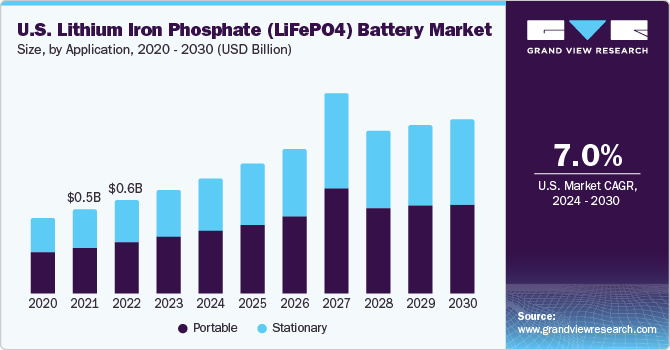
LiFePO4 will dominate stationary storage, with global market share growing to 40% by 2030 (CAGR 15-20%), driven by AI integration and higher density (up to 200 Wh/kg). Sodium-ion is poised for breakthrough, with energy density improving to 180 Wh/kg and market value reaching $5-10B by 2030 (CAGR 50%), as a lithium alternative amid supply shortages. Both will see hybrid advancements for grid-scale applications.
We're optimizing our portfolio for these trends—let's discuss how we can support your projects. Thoughts?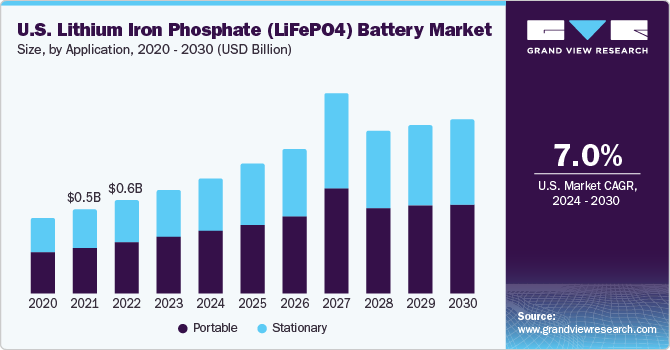
 LiFePO4 vs. Sodium-Ion Batteries for Energy Storage: Pros, Cons, and Future Trends
LiFePO4 vs. Sodium-Ion Batteries for Energy Storage: Pros, Cons, and Future Trends
 2025 Global Home Energy Storage Battery Market: Which Voltage is Best - 12V, 24V, or 48V?
2025 Global Home Energy Storage Battery Market: Which Voltage is Best - 12V, 24V, or 48V?



